Most Popular
 Facial Nerve Cancer and Parotid Tumor Surgery What You Need to Know
Facial Nerve Cancer and Parotid Tumor Surgery What You Need to Know
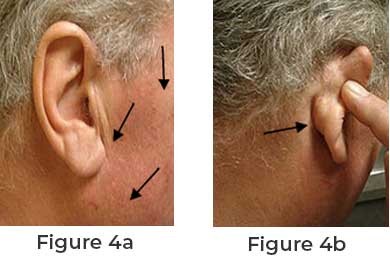
Facial nerve cancer is rare, with 500 US incidences annually. ...
 Parotidectomy and Facelift to Remove Parotid Gland and Rejuvenate the Appearance
Parotidectomy and Facelift to Remove Parotid Gland and Rejuvenate the Appearance
Parotidectomy and facelift are two distinct surgical procedures, each serving ...
 Know About the Parotid Cancer and Its Symptoms before Treatment
Know About the Parotid Cancer and Its Symptoms before Treatment
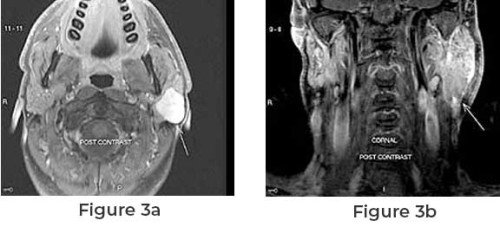
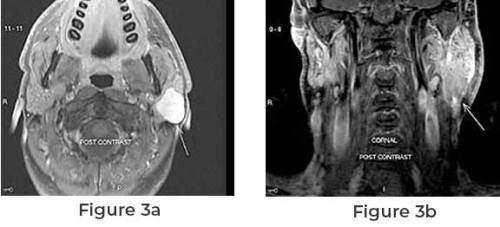
Parotid cancer is a rare form of cancer that originates ...



Parotid Tumor Surgery: Understanding the Procedure and Recovery
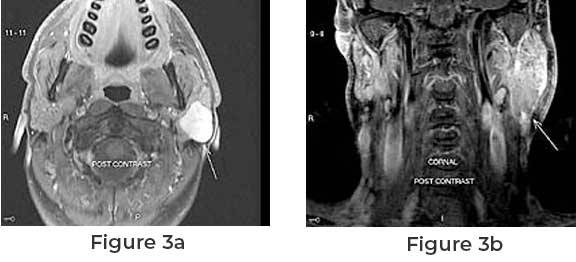
Parotid tumor surgery is a medical procedure performed to remove tumors from the parotid glands, which are the largest salivary glands located near the ears. Tumors in this area, while often benign (non-cancerous), can also be malignant (cancerous), necessitating removal for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
Diagnosis and Preparation
Before surgery, a thorough diagnosis is essential. This often involves imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT scans, or MRIs, as well as a biopsy, where a sample of the tumor is removed and tested for cancerous cells. Symptoms like swelling near the jaw or changes in facial movement may signal the presence of a parotid tumor. However, many benign tumors do not cause pain or noticeable changes.
The Surgical Procedure
The goal of parotid tumor surgery is to remove the tumor while preserving the function of the facial nerve, which runs through the parotid gland. The surgery is typically performed under general anesthesia and may last anywhere from 1 to 3 hours depending on the tumor’s size and location.
A common approach is to make an incision near the ear, where the tumor is accessed and carefully excised. In cases of benign tumors, only the tumor is removed, while in cases of malignant tumors, surrounding tissues may also be taken out to ensure all cancerous cells are eliminated.
If the tumor is located near or involving the facial nerve, the surgeon must take extra caution to avoid nerve damage. In some cases, nerve repair or reconstruction may be required post-surgery.
Recovery
Recovery time after parotid tumor surgery varies. Most patients stay in the hospital for one to two days, depending on the complexity of the surgery. Swelling and bruising around the incision site are common and typically resolve within a few weeks. Pain management is provided, and physical therapy may be necessary to address any issues with facial movement.
Patients are advised to avoid strenuous activities for several weeks post-surgery. Follow-up appointments are essential to monitor recovery and check for any signs of recurrence of the tumor, especially in cases of malignant growths.
In conclusion, parotid tumor surgery is a highly effective treatment for removing tumors in the parotid glands. With proper care, most patients can expect a good recovery, although the risk of complications, such as facial nerve damage, remains a concern.